
The variance is calculated the same way in case of both marginal and absorption costing systems. Specifically, fixed overhead variance is defined as the difference between standard cost and fixed overhead allowed for the actual output achieved and the actual fixed overhead cost incurred. The fixed factory overhead variance represents the difference between the actual fixed overhead and the applied fixed overhead.
Limitations of Standard Costing & Variance Analysis
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. Double Entry Bookkeeping is here to provide you with free online information to help you learn and understand bookkeeping and introductory accounting. This means that they must have had an unexpected earning of $80,000 positively affecting the financial statements.
What is a variable overhead variance?
The budgeted production volume here is also referred to as the normal capacity of the company or the existing facility in the production. Likewise, if the actual production exceeds the normal capacity, the result is favorable fixed overhead volume variance and vice versa. If the actual production volume is higher than the budgeted production, the fixed overhead volume variance is favorable.
What is Variance Analysis? Definition, Explanation, 4 Types of Variances
The fixed factory overhead variance represents the difference between the actual fixed overhead and the applied fixed overhead. This variance would be posted as a credit to the fixed overhead budget variance account. The amount of expense related to fixed overhead should (as the name implies) be relatively fixed, and so the fixed overhead spending variance should not theoretically vary much from the budget. However, if the manufacturing process reaches a step cost trigger point where a whole new expense must be incurred, this can cause a significant unfavorable variance. Also, there may be some seasonality in fixed overhead expenditures, which may cause both favorable and unfavorable variances in individual months of a year, but which cancel each other out over the full year.
(ii) Volume Variance
By contrast, efficiency variance measures efficiency in the use of the factory (e.g., machine hours employed in costing overheads to the products). In this case, the variance is favorable because the actual costs are lower than the standard costs. In August, the company ABC which is a manufacturing company has produced 950 units of goods in the production. However, the company ABC has the normal capacity of 1,000 units of production for August as they are scheduled to produce in the budget plan.
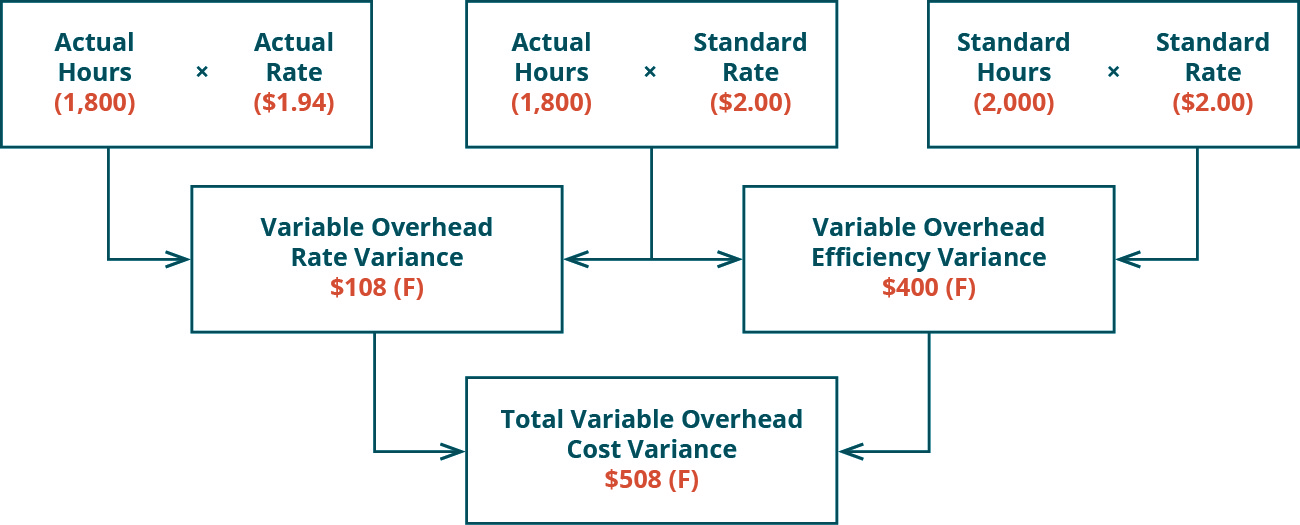
- Variable Overhead Spending Variance is essentially the difference between what the variable production overheads actually cost and what they should have cost given the level of activity during a period.
- Notice that fixed overhead remains constant at each of the production levels, but variable overhead changes based on unit output.
- Recall that the fixed manufacturing overhead costs (such as the large amount of rent paid at the start of every month) must be assigned to the aprons produced.
- Often, explanation of this variance will need clarification from the production supervisor.
- As an example of an unfavorable fixed overhead spending variance, a passing tornado delivers a glancing blow to the production facility of Hodgson Industrial Design, resulting in several hundred roofing tiles being blown off.
- The company can calculate fixed overhead volume variance with the formula of standard fixed overhead applied to actual production deducting the budgeted fixed overhead.
What causes an unfavorable fixed overhead budget variance?
Notice that fixed overhead remains constant at each of the production levels, but variable overhead changes based on unit output. If Connie’s Candy only produced at 90% capacity, for example, they should expect total overhead to be $9,600 and a standard overhead rate of $5.33 (rounded). If Connie’s Candy produced 2,200 units, they should expect total overhead to be $10,400 and a standard overhead rate of $4.73 (rounded). In addition to the total standard overhead rate, Connie’s Candy will want to know the variable overhead rates at each activity level. The standard overhead rate is the total budgeted overhead of \(\$10,000\) divided by the level of activity (direct labor hours) of \(2,000\) hours.
We will discuss how to report the balances in the variance accounts under the heading What To Do With Variance Amounts. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. Chartered accountant Michael Brown is the founder and CEO of Double Entry Bookkeeping. He has worked as an accountant and consultant for more than 25 years and has built financial models for all types of industries.
This type of variance is calculated separately for direct variable expenses and overhead variable expenses. Costing system wherein fixed manufacturing overhead is allocated to (or absorbed by) products being manufactured. definition of adjusted gross income This system, which treats fixed manufacturing costs as a product cost, is required for external financial statements. In case of fixed overhead, the budgeted and flexible budget figures are exactly the same.
Standard fixed overhead applied to actual production is the fixed overhead cost that is applied to the actual production volume using the standard fixed overhead rate. Interpretation of the variable overhead rate variance is often difficult because the cost of one overhead item, such as indirect labor, could go up, but another overhead cost, such as indirect materials, could go down. Often, explanation of this variance will need clarification from the production supervisor.